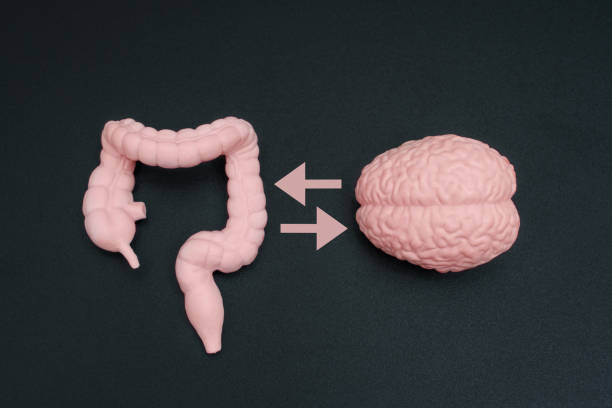
In recent years, scientists and health experts have discovered that the gut does much more than digest food—it also plays a crucial role in our mental health. The connection between the gut and the brain, often referred to as the gut-brain axis, shows how our digestive system and emotional well-being are closely linked.
Let’s explore how gut health impacts the mind and what you can do to support both.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
The gut is home to trillions of bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiome. These microorganisms help regulate digestion, strengthen the immune system, and even produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine—the same chemicals responsible for mood regulation.
When the gut is healthy, communication between the brain and digestive system runs smoothly. But when the gut is unbalanced, it can lead to issues like anxiety, stress, and even depression.
How Gut Health Affects Mental Well-Being
1. Production of Neurotransmitters
Nearly 90% of the body’s serotonin, often called the “happy hormone,” is produced in the gut. A healthy microbiome ensures steady production, helping stabilize mood and emotions.
2. Impact on Stress Levels
Research shows that gut bacteria can influence how the body responds to stress. An unhealthy gut may increase cortisol levels, making people more prone to anxiety and mood swings.
3. Connection to Inflammation
An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to inflammation, which is increasingly linked to mental health conditions like depression. Reducing gut inflammation often leads to improved emotional well-being.
4. Sleep and Cognitive Function
Gut health also plays a role in regulating sleep patterns and brain function. Poor gut balance can disrupt sleep quality, which in turn affects mood, focus, and overall mental health.
Tips to Improve Gut and Mental Health
Eat a Fiber-Rich Diet
Foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains feed the good bacteria in your gut, supporting a balanced microbiome.
Include Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables, along with prebiotics like garlic and bananas, help maintain a diverse gut environment.
Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration improves digestion and helps gut bacteria thrive.
Manage Stress
Mindfulness, meditation, and exercise reduce stress, protecting both gut health and mental well-being.
Limit Processed Foods
High-sugar and high-fat diets can disrupt gut bacteria, leading to negative effects on mood and energy.
The Takeaway
The saying “you are what you eat” holds more truth than ever. A healthy gut not only benefits digestion but also plays a direct role in shaping your emotional health and resilience. By nurturing your gut microbiome through diet, lifestyle, and stress management, you can create a positive cycle that supports both your body and mind.